Starting with supply chain management, this paragraph sets the stage for a deep dive into the world of optimizing business processes and enhancing efficiency through strategic planning and management.
Exploring the intricacies of supply chain planning, inventory management, logistics, transportation, and supplier relationships, this overview covers the essential components of successful supply chain operations.
Overview of Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management involves overseeing the flow of goods and services from the initial production stage to the final delivery to customers. It encompasses all the processes and activities involved in bringing a product or service to market.
Effective supply chain management is crucial for businesses as it helps optimize operations, reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance overall efficiency. By streamlining processes and ensuring smooth coordination between different stakeholders, companies can gain a competitive edge in the market.
Key Components of a Typical Supply Chain, Supply chain management
- Procurement: Involves sourcing raw materials, components, or services needed for production.
- Production: Includes the actual manufacturing of goods or the delivery of services.
- Inventory Management: Focuses on controlling and tracking inventory levels to prevent stockouts or overstock situations.
- Logistics: Deals with the transportation and distribution of products from one point to another.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Establishing strong partnerships with suppliers to ensure a smooth supply chain flow.
Supply Chain Planning: Supply Chain Management
Supply chain planning is a crucial process in managing the flow of goods and services from the point of origin to the point of consumption. It involves creating a strategic roadmap to ensure that products are delivered to customers efficiently and effectively.
Demand Forecasting in Supply Chain Planning
Demand forecasting plays a crucial role in supply chain planning by predicting future demand for products or services. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and customer behavior, companies can estimate the quantity of goods needed to meet customer demand. This information helps in making informed decisions about production, inventory levels, and distribution strategies.
- Forecasting accuracy is essential for minimizing stockouts or overstock situations, which can lead to increased costs and customer dissatisfaction.
- Utilizing advanced forecasting models and data analytics can improve the accuracy of demand forecasts, allowing companies to optimize their supply chain operations.
- Collaboration with suppliers, distributors, and other partners in the supply chain is also crucial in demand forecasting to share information and align strategies.
Technology in Optimizing Supply Chain Planning
Technology plays a significant role in optimizing supply chain planning by providing tools and systems to streamline processes, improve visibility, and enhance decision-making.
Advanced supply chain planning software can help companies analyze data, simulate different scenarios, and make real-time adjustments to meet changing demand patterns.
- Automation of routine tasks such as order processing, inventory management, and transportation planning can reduce lead times and operational costs.
- Integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensors in supply chain operations can provide real-time tracking of goods, monitor inventory levels, and identify potential bottlenecks in the supply chain.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, trends, and opportunities for improvement in supply chain planning.
Inventory Management
Inventory management plays a crucial role in supply chains by ensuring the right amount of products are available at the right time to meet customer demand while minimizing costs associated with excess inventory.
Different Inventory Management Strategies
- Just-In-Time (JIT): This strategy involves receiving goods only as they are needed in the production process, reducing storage costs and minimizing excess inventory.
- ABC Analysis: This method categorizes inventory into three groups based on value, with “A” items being the most valuable and closely monitored, “B” items having moderate value and control, and “C” items being low-value and managed less strictly.
- Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI): In VMI, the supplier manages the inventory levels for the buyer, ensuring optimal stock levels are maintained without the buyer having to actively monitor inventory.
Impact of Efficient Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management leads to reduced carrying costs, minimized stockouts, improved order fulfillment rates, and increased customer satisfaction. By optimizing inventory levels and implementing the right strategies, businesses can enhance their overall operations and profitability.
Logistics and Transportation
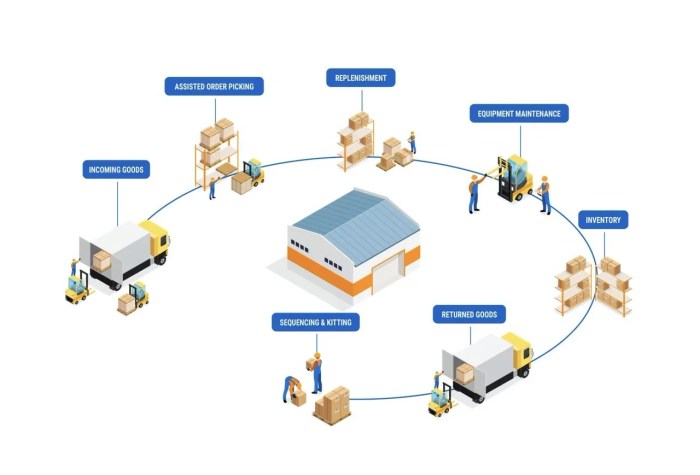
Logistics and transportation play a crucial role in supply chain management by ensuring the timely and efficient movement of goods from suppliers to customers. Logistics involves the coordination of all activities related to the flow and storage of goods, while transportation focuses on physically moving these goods from one point to another.
Challenges in Logistics and Transportation
- Inventory Management: Ensuring the right amount of inventory is available at the right time and place can be a challenge, leading to stockouts or excess inventory.
- Transportation Costs: Rising fuel prices and fluctuating transportation costs can impact the overall supply chain budget.
- Global Supply Chains: Managing logistics and transportation across international borders involves dealing with complex regulations, customs, and documentation.
- Environmental Impact: Balancing the need for efficient transportation with sustainability goals poses a challenge in reducing carbon emissions and environmental impact.
Innovative Transportation Solutions
- Intermodal Transportation: Utilizing multiple modes of transportation such as rail, road, and sea to optimize efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Real-Time Tracking: Implementing technology solutions like GPS tracking and RFID tags to monitor shipments in real-time and improve visibility.
- Collaborative Shipping: Partnering with other companies to share transportation resources and reduce costs through consolidated shipments.
- Last-Mile Delivery Solutions: Implementing innovative last-mile delivery options such as drones, autonomous vehicles, or crowdsourced delivery to enhance customer satisfaction.
Supplier Relationship Management
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) is the process of managing the interactions and relationships between a company and its suppliers. It plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and efficient supply chain operation by fostering collaboration, transparency, and mutual trust.
Building and Maintaining Strong Supplier Relationships
Building and maintaining strong supplier relationships require a strategic approach that involves clear communication, mutual respect, and a focus on long-term value creation. Some strategies for achieving this include:
- Establishing clear expectations and performance metrics
- Regular communication and feedback
- Creating win-win partnerships through collaboration
- Investing in supplier development and training
Benefits of Collaborative Supplier Relationships
Collaborative supplier relationships offer several benefits that can positively impact supply chain performance, such as:
- Improved supply chain visibility and transparency
- Enhanced quality and consistency of supply
- Increased innovation and product development
- Reduced lead times and inventory holding costs