Investment strategy sets the stage for financial success – let’s dive into the world of smart investing with this guide.
Introduction to Investment Strategy
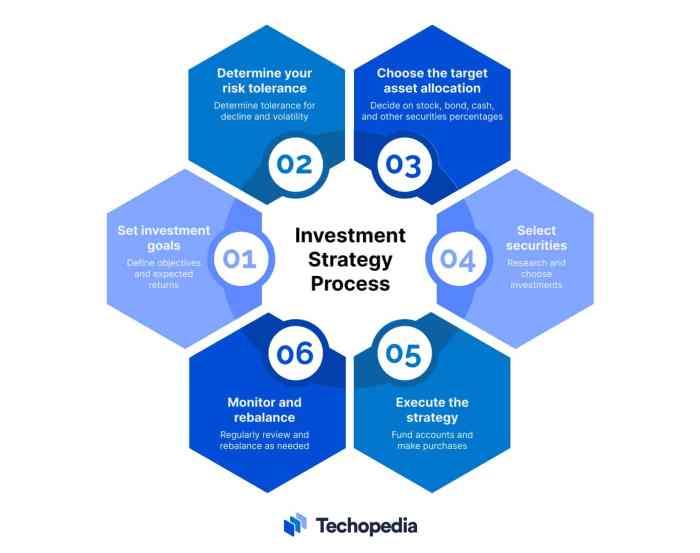
Investment strategy is a plan or approach used to guide an individual or organization in making investment decisions to achieve specific financial goals. It involves analyzing risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial objectives to determine the best way to allocate resources for maximum return.
Having a well-defined investment strategy is crucial because it helps investors stay focused, disciplined, and organized in their financial decisions. It also provides a roadmap for making informed choices based on research, analysis, and market conditions.
Types of Investment Strategies
- Long-Term Investing: This strategy involves buying and holding investments for an extended period, typically five years or more. It aims to capitalize on the long-term growth potential of assets.
- Value Investing: Value investors look for undervalued stocks or assets trading below their intrinsic value, with the belief that they will eventually increase in price.
- Dividend Growth Investing: Investors focus on companies that have a history of consistently increasing their dividend payouts over time, aiming to generate a steady income stream.
- Growth Investing: This strategy involves investing in companies with high growth potential, even if they may be trading at a premium. The goal is to benefit from capital appreciation.
Fundamental Analysis in Investment Strategy
Fundamental analysis is a method used by investors to evaluate the intrinsic value of a stock or security. It involves analyzing financial statements, economic indicators, market trends, and other relevant data to assess the health and performance of a company.
Fundamental analysis helps in forming an investment strategy by providing insights into the true value of a stock. By examining key financial metrics and market factors, investors can make informed decisions about buying, holding, or selling a particular security.
Key Fundamental Analysis Metrics
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: This ratio compares a company’s stock price to its earnings per share, providing insight into how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings.
- Revenue Growth: Examining the growth rate of a company’s revenue over time can indicate its ability to generate income and expand its operations.
- Profit Margin: The profit margin shows the percentage of revenue that translates into profit, highlighting the efficiency of a company’s operations.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: This ratio measures a company’s financial leverage by comparing its debt to its equity, indicating its ability to repay debt obligations.
- Dividend Yield: The dividend yield represents the annual dividend payment as a percentage of the stock price, reflecting the return on investment through dividends.
Technical Analysis in Investment Strategy
Technical analysis is a method used by investors to evaluate investments and identify trading opportunities by analyzing statistical trends gathered from trading activity, such as price movement and volume.
Role of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis plays a crucial role in investment strategy by providing insights into the historical price movements of a security, helping investors make informed decisions based on past performance and market trends.
- Identifying entry and exit points for trades
- Assessing market sentiment and investor psychology
- Recognizing patterns and trends in price movements
Complementing Fundamental Analysis
Technical analysis complements fundamental analysis by offering a different perspective on investment opportunities. While fundamental analysis focuses on the intrinsic value of a security, technical analysis looks at historical price data to predict future price movements.
Common Technical Indicators
There are several technical indicators used in developing investment strategies, including:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Averages closing prices over a specified period to identify trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the speed and change of price movements to indicate overbought or oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands: Used to identify volatility and potential price breakouts.
Risk Management in Investment Strategy
Investing in the financial markets can be lucrative, but it also comes with inherent risks. This is where risk management plays a crucial role in an investment strategy. By implementing effective risk management techniques, investors can protect their capital and optimize their returns.
Diversification
Diversification is a key risk management technique used by investors to spread their investment across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions. By diversifying their portfolio, investors can reduce the impact of any individual investment underperforming or facing losses. This strategy helps in minimizing the overall risk exposure.
Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are another important risk management tool that investors use to limit potential losses. By setting a predetermined price at which a security will be automatically sold, investors can protect themselves from significant declines in the value of their investments. This technique helps in controlling losses and preserving capital.
Risk Assessment
Conducting a thorough risk assessment is essential for effective risk management. Investors need to analyze the risk-return profile of each investment opportunity and assess the potential downside risks. By understanding the risks involved, investors can make informed decisions and adjust their portfolio accordingly to minimize potential losses.
Hedging
Hedging is a risk management strategy that involves using financial instruments like options and futures to offset potential losses in the market. By taking an opposite position to their existing investments, investors can protect themselves from adverse market movements and volatility. Hedging helps in reducing the overall risk exposure in a portfolio.
Diversification in Investment Strategy

Diversification is a key concept in investment strategy that involves spreading your investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce risk and maximize returns. By diversifying your investment portfolio, you can potentially minimize the impact of a decline in one particular investment on your overall portfolio.
Significance of Diversification
Diversification plays a crucial role in mitigating risk in an investment portfolio. It helps to protect against the volatility of individual assets by spreading investments across a variety of assets. This way, if one asset underperforms, the potential losses can be offset by the gains in other assets.
- Diversification reduces the concentration risk associated with having all your investments in one asset or industry. By spreading your investments, you can lower the impact of negative events on your portfolio.
- It can also improve the overall risk-adjusted returns of your portfolio by smoothing out the fluctuations in value that individual investments may experience.
- Furthermore, diversification can provide exposure to a wider range of opportunities, allowing you to benefit from the growth potential of different sectors and regions.
Benefits of Diversifying Investment Holdings
When it comes to diversifying your investment holdings, there are several benefits to consider:
- Reduced Risk: Diversification helps to lower the overall risk of your portfolio by spreading investments across different assets.
- Enhanced Returns: By diversifying, you can potentially improve the risk-adjusted returns of your portfolio over the long term.
- Increased Flexibility: Diversification offers the flexibility to adjust your portfolio based on changing market conditions or investment opportunities.
Ways to Achieve Diversification, Investment strategy
There are various ways to achieve diversification in an investment strategy:
- Asset Allocation: Allocate your investments across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
- Industry Diversification: Spread your investments across various industries to reduce exposure to sector-specific risks.
- Geographic Diversification: Invest in different regions or countries to mitigate geopolitical risks and take advantage of global growth opportunities.